Eyelid ptosis: Causes and Significance
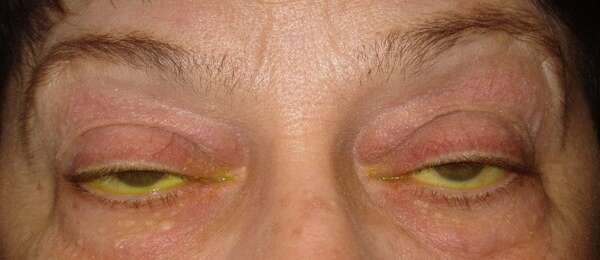
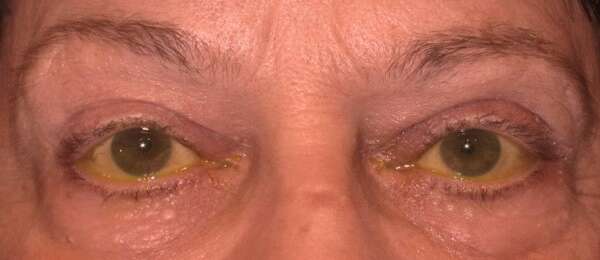
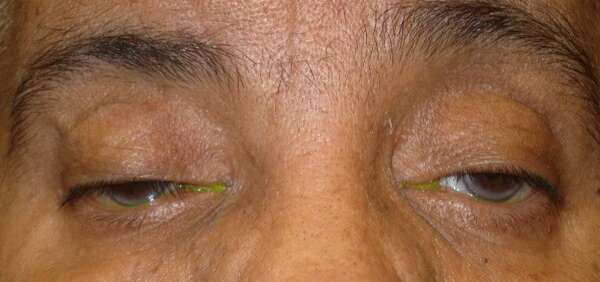
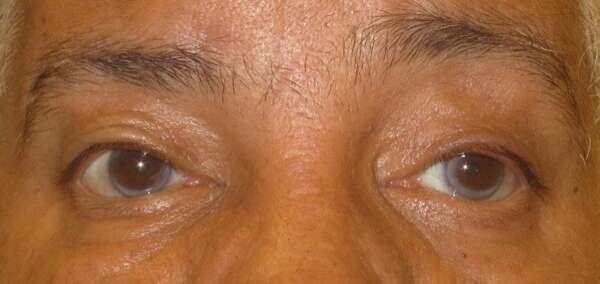
Droopy eyelid ptosis, or ptosis, refers to the drooping or falling of the upper eyelid, which can significantly impact both function and appearance. The primary underlying cause of ptosis is the inability of the levator muscle (levator aponeurosis) to lift the eyelid properly. This can lead to various degrees of eyelid droopiness, affecting one or both eyes. While ptosis is commonly associated with aging due to muscle deterioration, congenital cases can occur, where an individual is born with weakened or underdeveloped eyelid muscles.
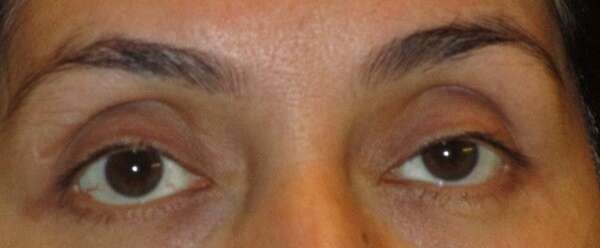
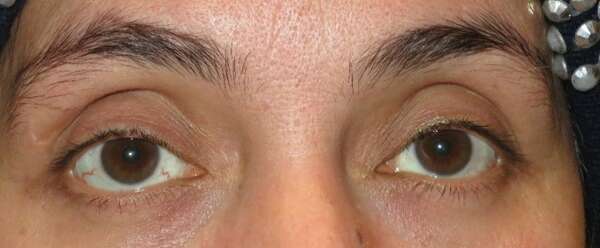
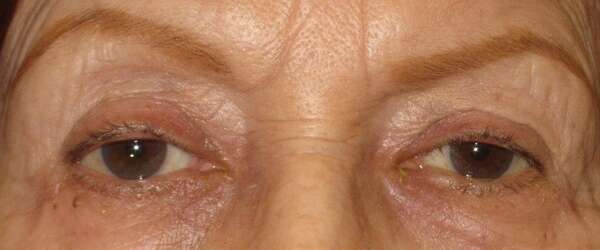
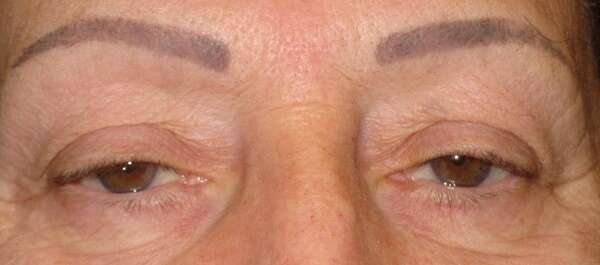
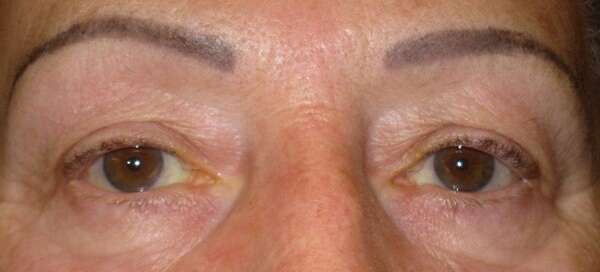
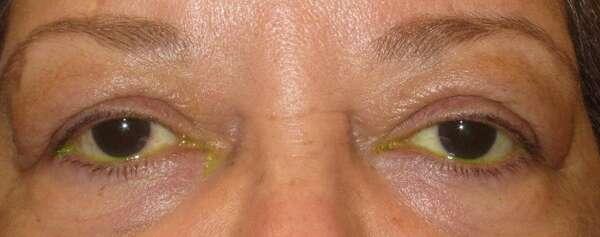
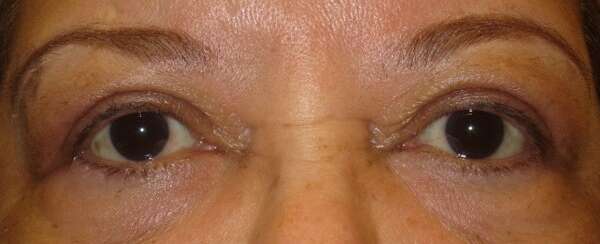
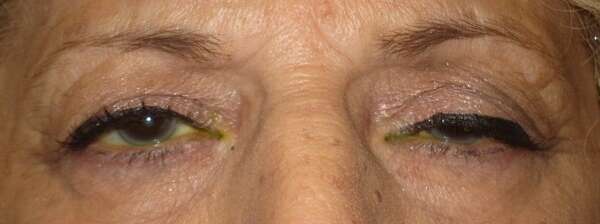
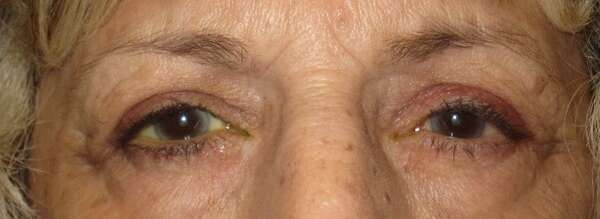
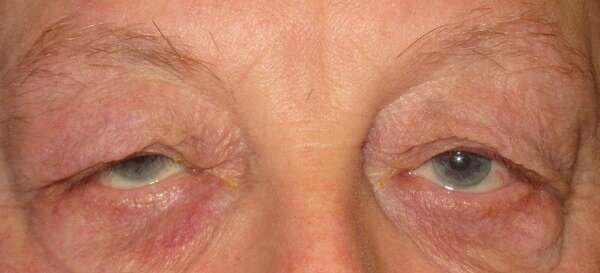
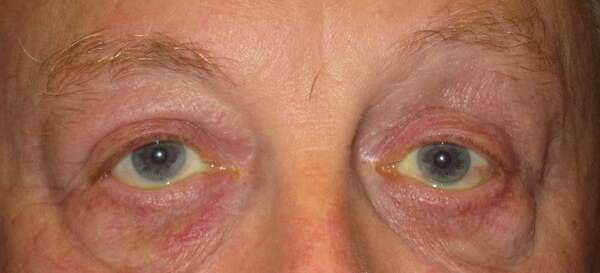
Before and After Surgical Droopy Eyelid Repair Procedure Comparison
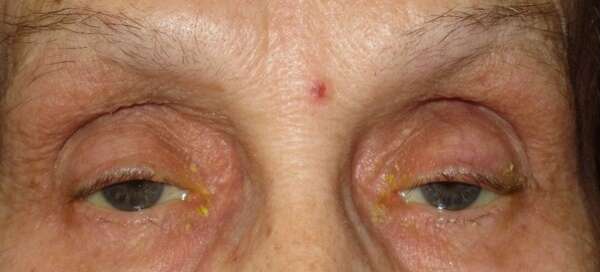
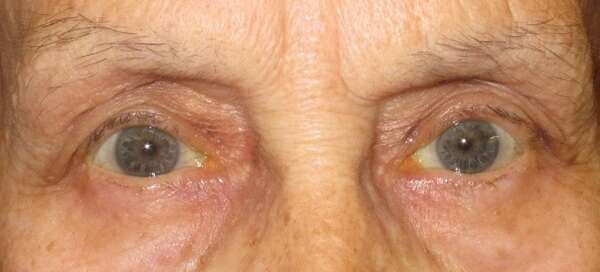
Causes and Risk Factors of Ptosis (Droopy eyelid)
- ⚕Age-Related Changes: The most prevalent form of ptosis arises in older adults as part of the natural aging process. Over time, the eyelid muscles can weaken, and the connection between the muscle and the eyelid (levator aponeurosis) can become loose or detached.
- ⚕Congenital Ptosis: Children can be born with ptosis due to underdeveloped levator muscles. Identifying and treating ptosis in children early is critical, as severe drooping can obstruct vision and potentially impair visual development. Untreated cases can lead to amblyopia, or “lazy eye,” or other permanent vision issues.
- ⚕Trauma or Nerve Damage: Ptosis may develop following damage to the muscle or nerves responsible for elevating the droopy eyelid. Injuries or trauma that affect these components can compromise eyelid function.
- ⚕Underlying Medical Conditions: Ptosis can also signal deeper health concerns. Diseases that affect nerve or muscle function, such as diabetes mellitus, myasthenia gravis, brain tumors, or lung tumors, can manifest with ptosis as an initial symptom. Myasthenia gravis, in particular, is an autoimmune disease that weakens voluntary muscles, impacting the eyelids and other muscle groups.
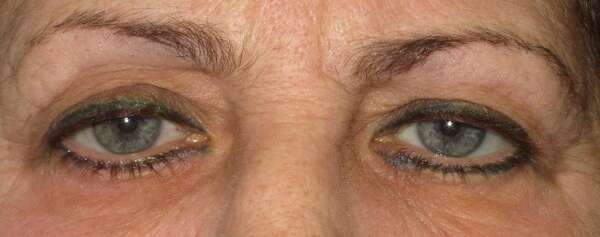
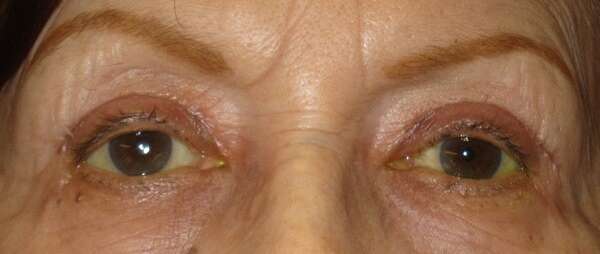
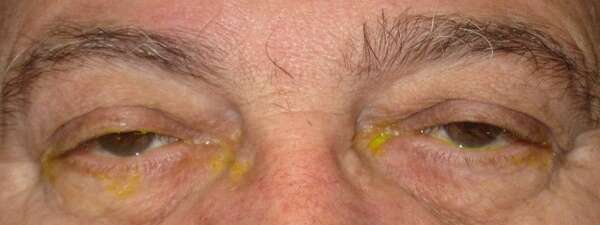
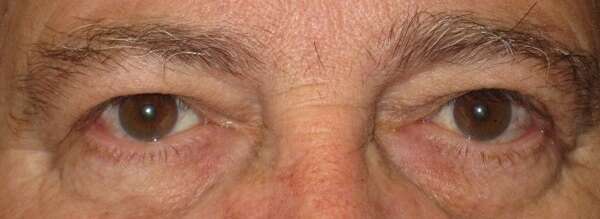
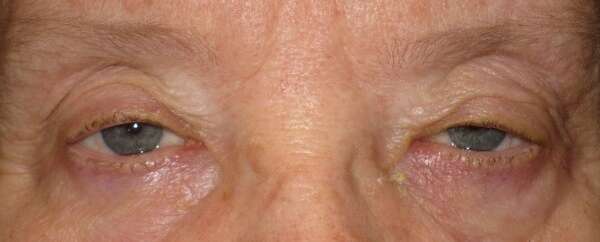
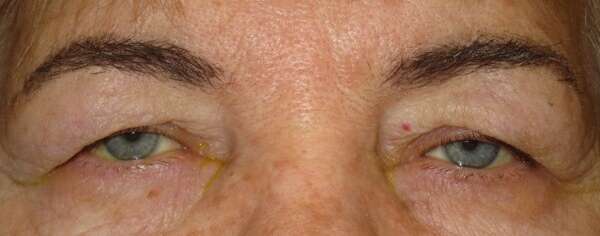
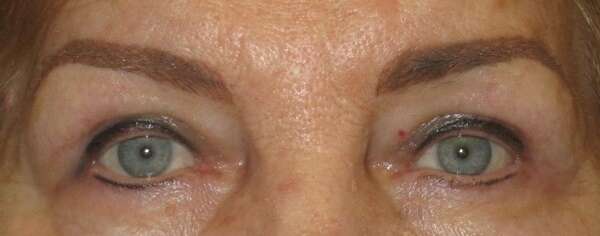
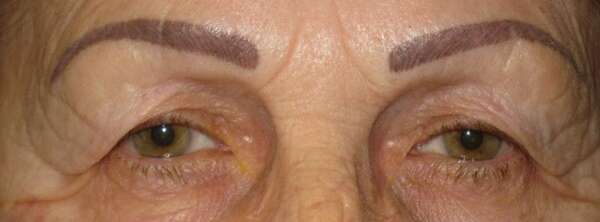
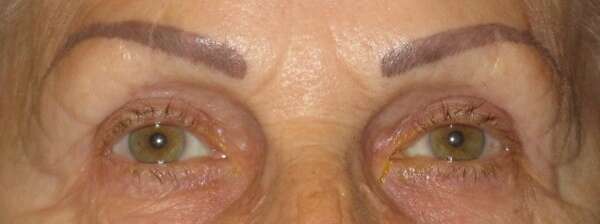
Before and After Surgical Procedure Comparison
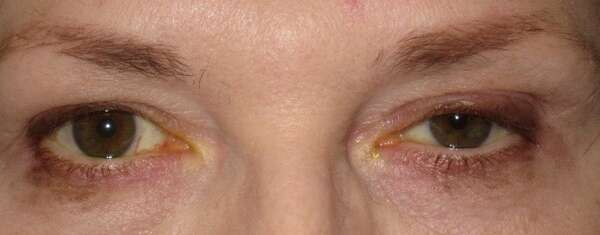
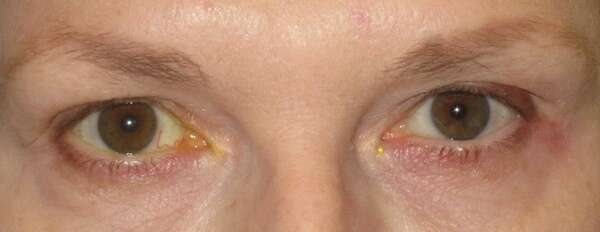
Droopy Eyelid Diagnosis and Clinical Evaluation
Accurate diagnosis requires a detailed medical history and thorough examination to exclude underlying conditions. The evaluation will often include:
- ⚕A physical exam.
- ⚕Assessment of eyelid function.
- ⚕Imaging or lab tests are sometimes used to identify any related systemic issues.
Determining the severity and cause of ptosis is essential for developing an effective treatment plan.
Surgical Solutions for Ptosis
Surgical intervention may be recommended when ptosis interferes with vision or is a cosmetic concern. The choice of procedure depends on the underlying cause, muscle function, and degree of drooping.
- ⚕Levator Resection: This standard procedure involves incision of the upper eyelid skin to access and tighten the levator muscle with sutures. The surgical scar is minimal and typically well-hidden in the natural eyelid crease, providing effective functional and aesthetic outcomes.
- ⚕Müller Muscle Resection: This approach is suitable for cases where the levator muscle has partial functionality. The surgery is performed from the inside of the droopy eyelid (conjunctival approach), ensuring no external scar is visible. This method can be effective for mild to moderate ptosis.
- ⚕Frontalis Sling Operation: A frontalis sling procedure may be the best option for patients with significantly weakened or damaged levator muscles. This technique connects the forehead muscle (frontalis) to the eyelid using a silicone rod or other biocompatible material. The forehead muscle’s contraction helps elevate the eyelid, compensating for the deficient levator function.
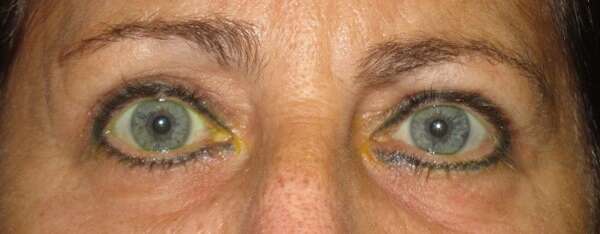
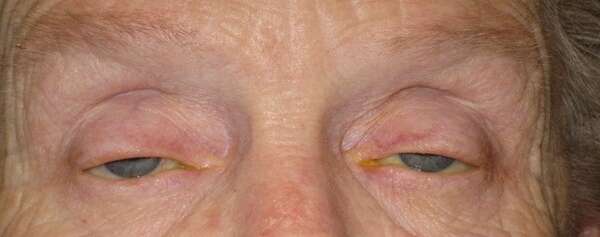
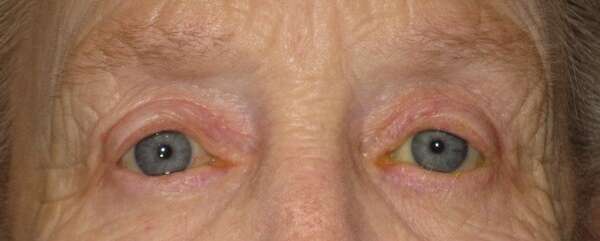
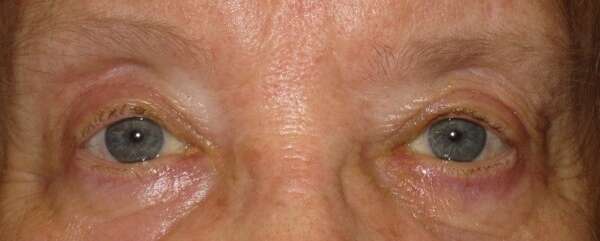
Before and After Surgical Procedure Comparison